Selecting the right adhesive for your engineering project is crucial for ensuring durability, reliability, and performance.
Adhesives play a key role in various applications, from aerospace and automotive to electronics and construction.
Also, you can use them for interesting DIY projects, which is the case with epoxy resin in woodworking.
With a plethora of options available, choosing the appropriate adhesive can be overwhelming. Here’s a guide to help you make an informed decision.
Understand the Substrates
The first step in choosing the right adhesive is to identify the materials you need to bond. Different adhesives are formulated to work with specific substrates, such as metals, plastics, glass, composites, or wood.
For instance, epoxies are well-suited for bonding metals and composites, while cyanoacrylates (super glues) work exceptionally well with plastics and rubber. Knowing the properties of your substrates will narrow down your choices.
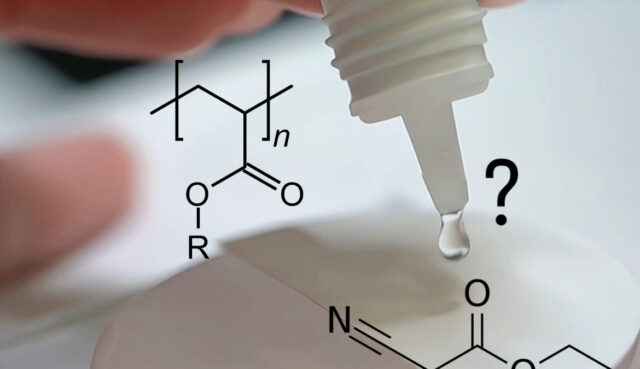
Evaluate the Environmental Conditions
Consider the environmental conditions to which the adhesive bond will be exposed. Factors such as temperature, humidity, UV exposure, and chemical exposure can significantly impact adhesive performance.
For high-temperature applications, such as in automotive or aerospace projects, you might need an adhesive with excellent thermal resistance, like a high-temperature epoxy. For outdoor applications, UV-resistant adhesives like certain silicones or polyurethanes are ideal.
Determine the Load Requirements
Understanding the load requirements of your project is essential. This includes both static and dynamic loads. If the bonded joint will be under constant stress or cyclic loading, you need an adhesive with high tensile strength and fatigue resistance.
Structural adhesives like epoxies and polyurethanes are commonly used for load-bearing applications. For less demanding applications, pressure-sensitive adhesives (PSAs) or hot melts might suffice.

Consider the Bonding Process
The bonding process itself can influence your choice of adhesive. Factors to consider include:
- Curing time ─ Some adhesives cure quickly, while others may take several hours or even days. Fast-curing adhesives like cyanoacrylates are suitable for applications requiring quick assembly, while slower-curing epoxies may be better for projects where precise alignment is crucial.
- Application method ─ Adhesives can be applied in various forms—liquid, paste, tape, or film. The method of application will depend on the size and shape of the bonding area, as well as the production process. For automated production lines, adhesive tapes or films can enhance efficiency.
- Surface preparation ─ Proper surface preparation is critical for optimal adhesion. Some adhesives require minimal preparation, while others may need extensive cleaning, abrasion, or the application of a primer.
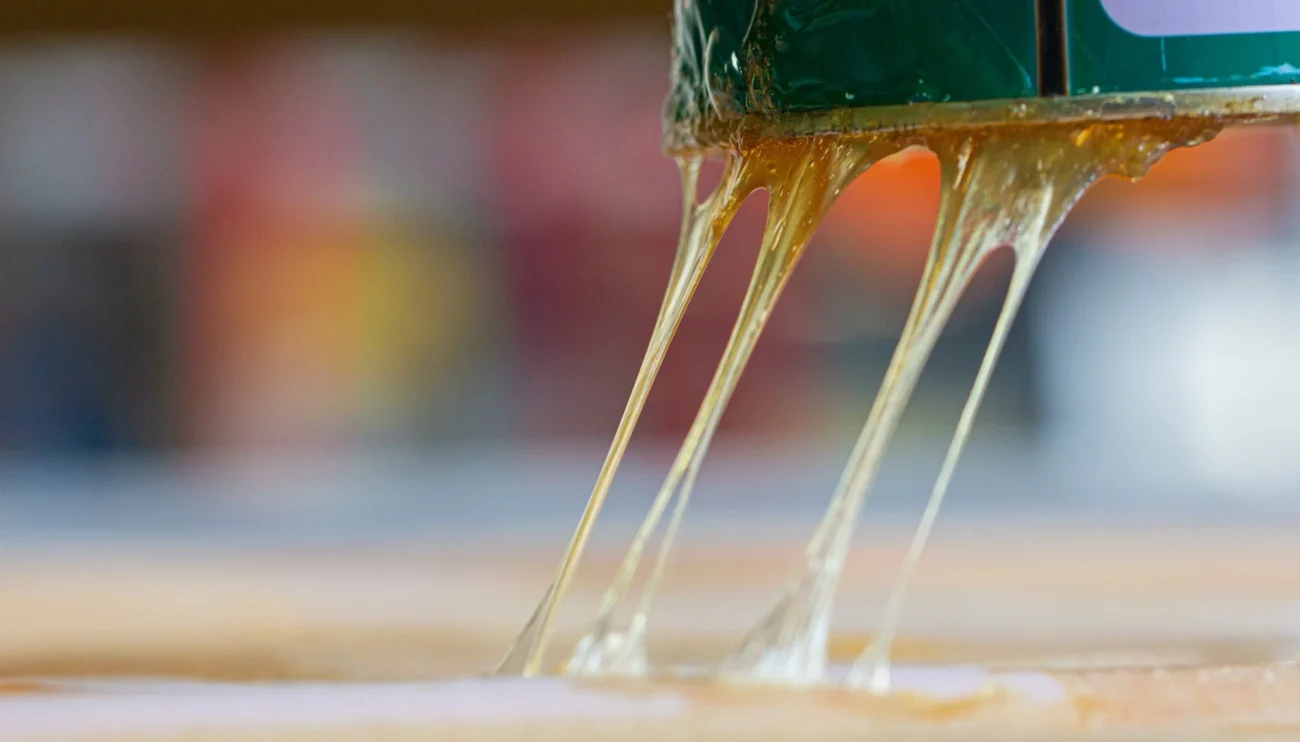

Evaluate the Adhesive Properties
Each adhesive type has unique properties that make it suitable for specific applications. Here are some common adhesives and their characteristics:
- Epoxies ─ Known for their strong bond and chemical resistance, epoxies are ideal for structural applications. They offer excellent mechanical strength and durability.
- Cyanoacrylates ─ These fast-setting adhesives are perfect for small, quick repairs and are effective on a variety of substrates, including plastics and rubber.
- Polyurethanes ─ Flexible and resistant to impact and vibration, polyurethanes are great for bonding dissimilar materials and for applications requiring a tough, resilient bond.
- Silicones ─ With excellent thermal stability and flexibility, silicones are used in applications requiring resistance to extreme temperatures and environmental conditions.
- Acrylics ─ Offering a good balance of strength and flexibility, acrylics are often used in automotive and electronic applications for their excellent bonding properties and resistance to environmental factors.

Testing and Validation
Before finalizing your adhesive choice, it’s important to conduct testing and validation. This may involve:
- Adhesion testing ─ To ensure the adhesive forms a strong bond with the substrates.
- Environmental testing ─ To verify the adhesive’s performance under expected environmental conditions.
- Mechanical testing ─ To assess the bond’s strength and durability under load.
Conclusion
Selecting the right adhesive for your engineering project involves careful consideration of the substrates, environmental conditions, load requirements, bonding process, and adhesive properties.
By thoroughly evaluating these factors and conducting appropriate testing, you can ensure a successful and durable bond, ultimately leading to the success of your project.